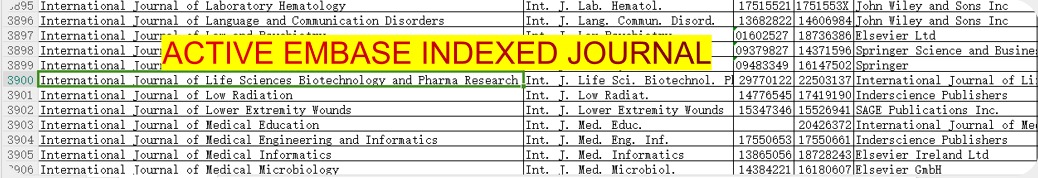
International Journal of Life Sciences Biotechnology and Pharma Research
International Journal of Life Sciences Biotechnology and Pharma Research (IJLBPR) is a monthly peer reviewed international indexed
journal.
It publishes original research work that contributes significantly to further enhance the scientific knowledge in Medical Sciences,
Life sciences, Dental, Pharmaceutical Sciences and Biotechnology. All papers will be blind reviewed and accepted papers will
be published monthly which is available online (open access) and in printed version.
Journal follows the Latest Guidelines of NMC as it is indexed in EMBASE.
You can verify EMBASE indexing of journal by downloading the list of all journals indexed in EMBASE
(Click here or on the image to go to Embase website to download list of all journals)